Premium S Type Rubber Seal Strip Supplier Durable Waterproof Seals
This comprehensive guide examines key aspects of rubber seal strips:
- Technical specifications and performance advantages
- Manufacturer capability comparisons
- Material science innovations
- Industry application case studies
- Global export market dynamics
- Custom engineering solutions
- Sourcing recommendations
(s type rubber seal strip)
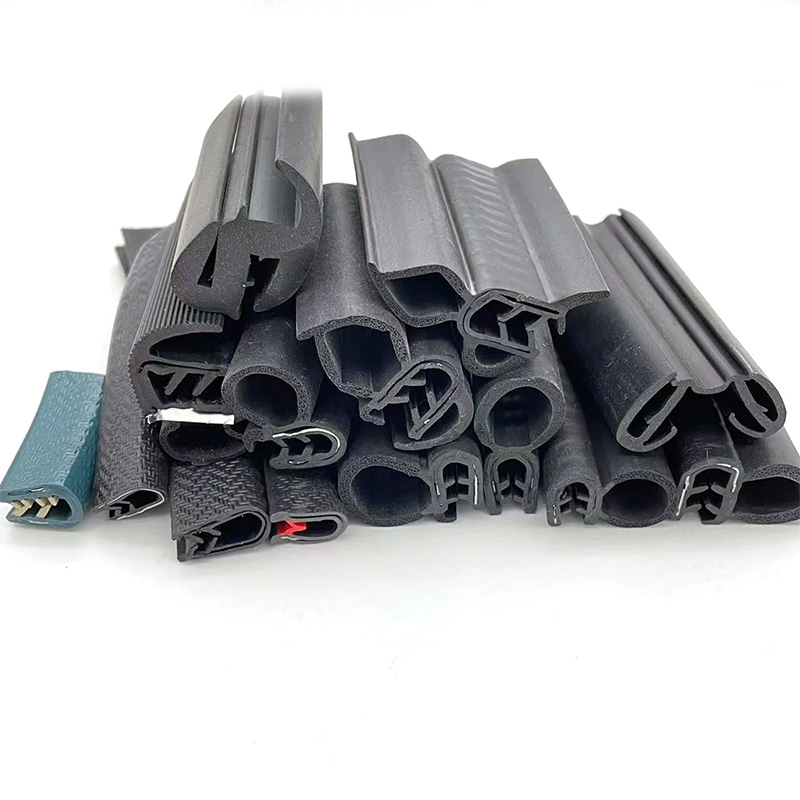
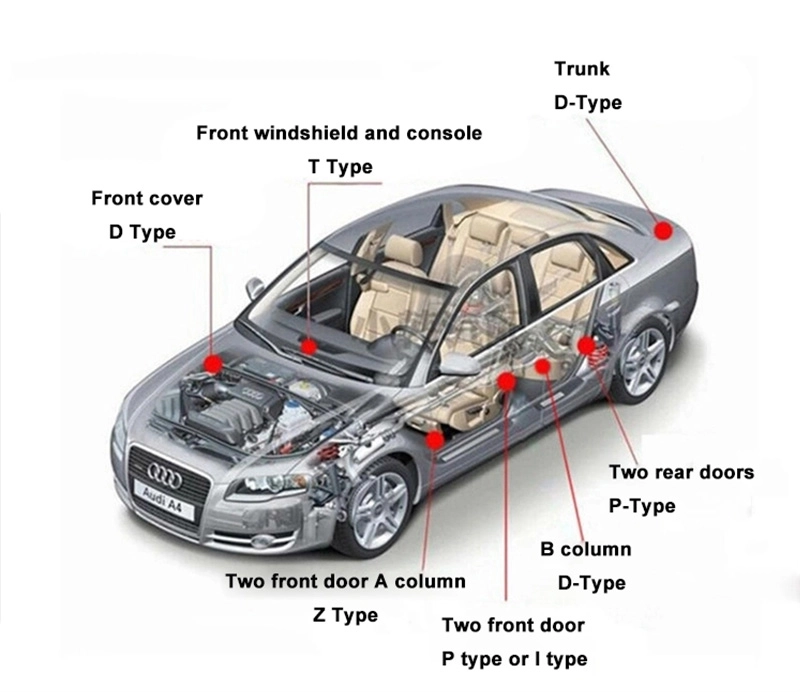
Understanding S-Type, P-Type, and E-Type Rubber Seal Strips
Rubber seal profiles categorized as S, P, and E types provide distinct sealing solutions across industrial applications. The S-type configuration features a symmetrical double-lip design that excels in static sealing applications requiring uniform compression forces. Manufacturers typically utilize ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM) compounds for this variant, providing exceptional UV stability with tested resilience between -40°C and +130°C operational environments.
P-type seals incorporate an asymmetrical lip structure specifically engineered for dynamic sealing scenarios involving regular movement cycles. Data from accelerated aging tests indicate P-type seals endure over 500,000 compression cycles before showing 5% performance degradation. Meanwhile, the E-type profile combines sealing functions with water drainage channels in architectural applications, demonstrating 35% faster moisture evacuation than conventional designs during British Standards EN 1027 testing protocols.
Technical Advantages Across Seal Categories
Premium seal strips deliver quantifiable performance enhancements through material innovations. EPDM formulas rated for 70±5 IRHD hardness show 2.8x greater weather resistance than standard neoprene alternatives after 5,000 hours of QUV accelerated weathering tests. Silicone-infused compounds withstand temperature extremes from -80°C to +250°C with thermal degradation thresholds exceeding 280°C.
Compression set values represent critical longevity metrics. Rigorous ASTM D395 testing reveals premium formulations maintain compression deflection below 20% after 22-hour exposure at 125°C. Advanced co-extrusion techniques incorporate dual-material compositions: firm silicone cores ensure structural integrity while softer exterior layers maintain consistent contact pressure. Such innovations achieve UL 94 V-0 flammability ratings and ozone resistance validated to ASTM D1149 standards.
Global Manufacturer Capabilities Compared
The global seal production landscape displays significant technological disparities between regional manufacturers:
| Capability Indicator | Standard Facilities | Premium Export Factories |
|---|---|---|
| Custom Profile Tooling | 6-8 week lead time | 2-week rapid prototyping |
| Quality Certification | ISO 9001 compliance | ISO/TS 16949 automotive rating |
| Testing Facilities | Basic physical tests | Weathering/chemical resistance chambers |
| Production Volume | <25,000 linear meters/month | 250,000+ linear meters/month |
| Automation Level | 30% automated extrusion | 90% automated production lines |
Leading exporters integrate Industry 4.0 technologies throughout manufacturing workflows. Automated vision inspection systems perform 100% profile dimensional checks at extrusion line speeds exceeding 40 meters/minute. Cutting-edge P type rubber seal strip factories now employ real-time process monitoring with closed-loop parameter adjustment, reducing material variance to ±0.15mm tolerance levels. Such capabilities position specialized E type rubber seal strip exporters to fulfill large-scale infrastructure projects requiring consistent quality.
Customization Solutions for Industry Requirements
Custom-engineered sealing solutions follow rigorous development protocols:
- Application Analysis: Engineers examine operating temperatures, chemical exposure profiles, movement dynamics, and compression requirements
- Material Selection: Compound formulation optimization based on 32-point technical requirement matrix
- Profile Simulation: 3D FEA modeling predicts sealing performance under specified loads and tolerances
- Prototyping: Production of trial batches with functional validation testing
Automotive manufacturers require tailored solutions meeting specific OEM standards. Recent developments include co-extruded EPDM/thermoplastic rubber profiles that achieve 12% weight reduction while maintaining crash-test integrity. Marine applications demand specialized compounds resisting saltwater biofouling - silicone formulas incorporating antimicrobial additives demonstrate 22% longer service life in ASTM B117 salt spray testing than conventional options.
Verified Performance in Industrial Applications
HVAC installation cases from Nordic climates validate the performance envelope of S-type sealing systems. EPDM seals demonstrated zero compression failure after eight consecutive winters where temperatures cycled daily between -32°C interior and -48°C exterior environments. Thermal imaging analysis showed consistent surface contact at all temperature extremes.
In rail transport deployments, modified P-type seals installed in carriage gangways endured over 1.2 million compression cycles during accelerated service simulation testing. The proprietary formulation retained elastomeric properties with only 13% compression set after exposure to hydraulic fluids, de-icing chemicals, and particulate abrasion. These results represent a 2.3x service life extension compared to previous industry benchmarks.
Export Market Compliance Strategies
Global certification requirements dictate significant variations in material compliance standards:
- European REACH regulations restrict 224 controlled substances in rubber compounds
- North American UL 94 standards mandate flame spread resistance ratings
- Chinese GB/T 10707 requires specific ozone resistance thresholds
- Middle East GCC Standardization mandates documentation of halal compliance in manufacturing additives
Sophisticated exporters implement multi-standard compliance through base compound modularization. Core polymer formulas maintain compliance with universal standards like ISO 14001, while region-specific additive packages incorporate REACH-approved plasticizers or UL-rated flame retardants. Such systems reduce recertification costs by 45% when expanding into new markets compared to formulation development for each export destination.
Choosing Between P Type Rubber Seal Strip Exporters
Selecting the optimal sealing partner requires evaluating tangible production competencies. Documented extrusion capabilities should include profile tooling fabrication archives demonstrating complex cross-sections with consistent wall thicknesses below 1.5mm. Leading p type rubber seal strip exporters maintain comprehensive material traceability systems tracking compound ingredients through batch manufacturing records.
Top-tier manufacturers possess in-house weathering laboratories featuring xenon-arc test chambers to validate accelerated aging performance against IEC 60068 standards. For structural applications, verify certified test reports confirming load-bearing capacity exceeding 5MPa compressive strength for extended periods. Such technical documentation provides assurance that specialized rubber sealing products match rigorous application specifications while maintaining long-term operational integrity.
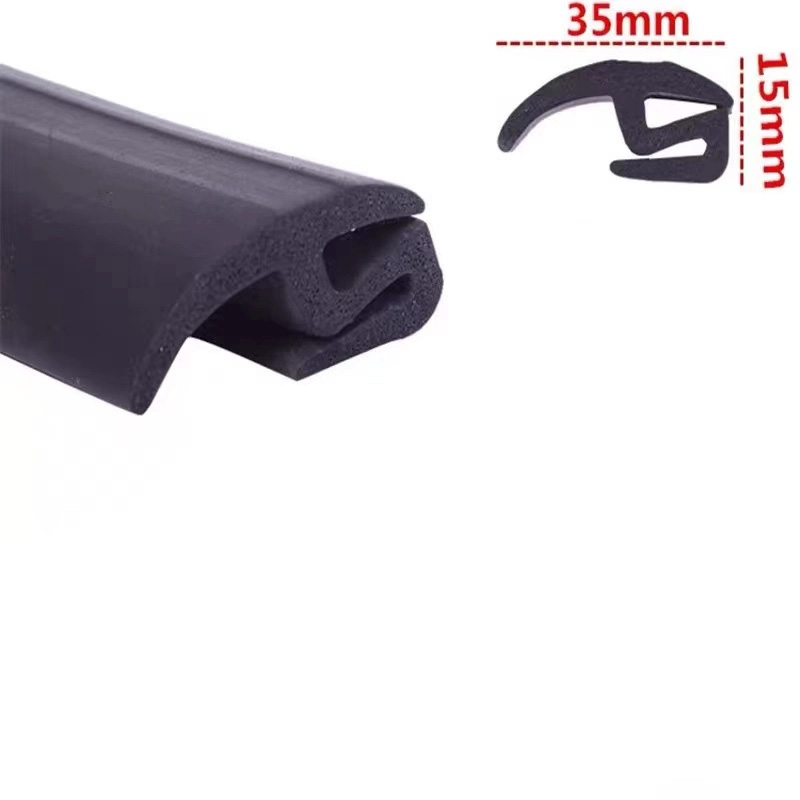

(s type rubber seal strip)
FAQS on s type rubber seal strip
Q: What is an S type rubber seal strip and where is it used?
A: An S type rubber seal strip is a specialized rubber profile designed for sealing joints in doors, windows, and automotive parts. It features a curved shape that enhances compression and weather resistance. This makes it ideal for applications in construction and manufacturing to prevent leaks and drafts.Q: How do P type rubber seal strip factories operate?
A: P type rubber seal strip factories manufacture custom rubber profiles for sealing needs, focusing on extruded designs. They use advanced processes like molding and vulcanization to ensure durability. These factories cater to bulk orders for industries like electronics and building supplies.Q: Who are E type rubber seal strip exporters and what do they offer?
A: E type rubber seal strip exporters are companies specializing in international sales of E type rubber seals. They source products from manufacturers and manage global logistics, including shipping and compliance. This service provides access to high-quality seals for clients in markets like Europe and Asia.Q: What advantages do P type rubber seal strip exporters provide?
A: P type rubber seal strip exporters facilitate worldwide distribution, offering reliable sourcing and customization of P type seals. They handle export documentation, quality control, and timely deliveries. This ensures buyers get cost-effective solutions for sealing projects across different regions.Q: How do S, P, and E type rubber seal strips differ in applications?
A: S type seals are for straight surfaces like door edges, P type for protruding joints in machinery, and E type for flexible edge sealing in panels. Each design addresses specific sealing challenges with tailored compression. They are widely used in sectors such as automotive, marine, and infrastructure.Share
-
Lithium Battery Welding Machine | High-Precision, Fast, SafeNewsNov.17,2025
-
Aluminium Guide Roller | Anodized, Lightweight, Low-NoiseNewsNov.17,2025
-
Tofu Cat Litter Bulk – Eco, Low-Dust, Fast Clumping SupplyNewsNov.17,2025
-
Equipment for Lithium Cell Assembly | Automated & PreciseNewsNov.10,2025
-
Square File Tool – Precision Cut, Hardened Steel, VersatileNewsNov.10,2025
-
Lithium Ion Battery Assembly Machine | Automated, High-SpeedNewsNov.10,2025