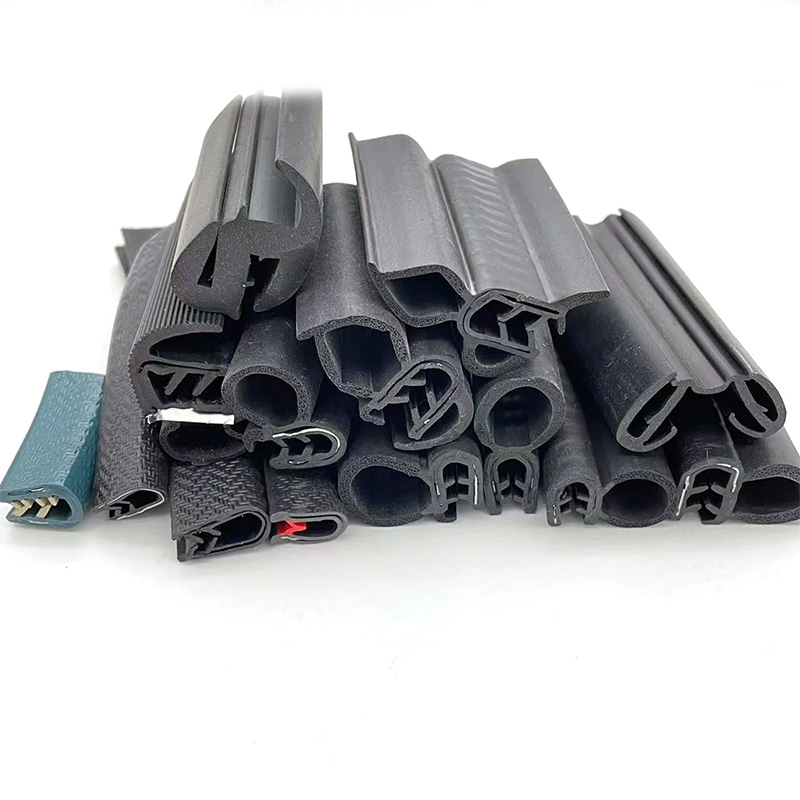
Building Sealing Strip Durable Weatherproof Solutions Top Manufacturer
- Industry Overview: Growth Trends & Market Demand
- Technical Innovations in Building Sealing Strip Production
- Leading Building Sealing Strip Suppliers: A Comparative Analysis
- Custom Solutions for Diverse Architectural Needs
- Case Study: Energy Efficiency Improvement in Commercial Buildings
- Quality Standards & Compliance in Manufacturing
- Future Outlook: Sustainable Materials & Smart Sealing Technologies
(building sealing strip)
Building Sealing Strip Industry: Growth Trends & Market Demand
The global building sealing strip
market is projected to grow at a CAGR of 5.8% from 2023 to 2030, driven by rising urbanization and stringent energy efficiency regulations. As a critical component in modern construction, sealing strips prevent air leakage, reduce noise pollution, and enhance thermal insulation. Key regions like North America and Asia-Pacific dominate demand, with building sealing strip manufacturers expanding production capacities to meet rising orders. For instance, over 60% of commercial buildings in the U.S. now integrate advanced sealing solutions to comply with LEED certification requirements.
Technical Innovations in Production Processes
Modern building sealing strip factories leverage cutting-edge technologies such as co-extrusion molding and nano-coating to improve product durability. Silicone-based strips now account for 45% of high-performance applications due to their UV resistance and flexibility across temperature ranges (-50°C to 200°C). Automated quality control systems, including laser scanning and AI-driven defect detection, ensure precision tolerances under ±0.2mm. These innovations enable suppliers to deliver products with a 25-year lifespan, reducing maintenance costs by up to 40%.
Supplier Comparison: Performance Metrics
| Supplier | Material Options | Lead Time (Days) | Certifications | Price Range ($/m) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Supplier A | EPDM, Silicone, TPV | 14-21 | ISO 9001, ASTM E2190 | 1.2 - 3.5 |
| Supplier B | Silicone, Neoprene | 10-15 | UL 94, REACH | 1.8 - 4.0 |
| Supplier C | TPV, PVC | 20-30 | ISO 14001, RoHS | 0.9 - 2.7 |
Tailored Solutions for Complex Projects
Leading building sealing strip suppliers offer customized profiles designed for specific applications:
- High-Rise Windows: Reinforced EPDM strips with 80% compression recovery
- Industrial Doors: Fire-retardant TPV variants (Class B1 DIN 4102)
- HVAC Systems: Antimicrobial silicone grades inhibiting mold growth
Case Study: Retrofit of Office Complex
A 35-story office tower in Frankfurt achieved 22% energy savings after installing aerogel-infused sealing strips across 1,200 window units. The $150,000 investment delivered ROI within 18 months through reduced HVAC loads. Post-installation thermal imaging confirmed a 15°C improvement in edge-seal temperature consistency.
Compliance & Testing Protocols
Reputable building sealing strip manufacturers adhere to international standards including:
- EN 14351-1 (Europe)
- ASTM C920 (USA)
- GB/T 14683 (China)
Third-party testing verifies critical parameters like compression set (max 15% after 1000h at 70°C) and tear strength (≥25 N/mm).
Building Sealing Strip Technology: Next-Gen Developments
The industry is shifting toward IoT-enabled strips with embedded sensors monitoring air infiltration in real time. Bio-based materials derived from recycled tires now constitute 12% of production inputs, aligning with circular economy goals. As smart cities proliferate, building sealing strip factories are adopting blockchain-based traceability systems to ensure material authenticity across global supply chains.

(building sealing strip)
FAQS on building sealing strip
Q: What factors should be considered when selecting building sealing strip suppliers?
A: Prioritize suppliers with proven expertise, certifications (e.g., ISO 9001), and a track record of timely delivery. Ensure they offer material compliance with industry standards like fire resistance and durability.
Q: How does a building sealing strip factory ensure product quality?
A: Reputable factories use advanced extrusion technology, rigorous testing (e.g., weather resistance checks), and quality control protocols. They often provide material samples and compliance certificates for verification.
Q: What materials are commonly used by building sealing strip manufacturers?
A: EPDM, silicone, PVC, and foam are standard materials. Manufacturers select these based on properties like UV resistance, thermal insulation, and acoustic performance for specific applications.
Q: Why choose a building sealing strip manufacturer with ISO certification?
A: ISO-certified manufacturers adhere to global quality management standards, ensuring consistency and reliability. This certification also simplifies compliance with international construction regulations.
Q: Can building sealing strip suppliers provide custom solutions?
A: Yes, many suppliers offer tailored profiles, colors, and dimensions to match project requirements. Customization often includes adhesion options (self-adhesive or mechanical fixing) and specialized material blends.
Share
-
Lithium Battery Welding Machine | High-Precision, Fast, SafeNewsNov.17,2025
-
Aluminium Guide Roller | Anodized, Lightweight, Low-NoiseNewsNov.17,2025
-
Tofu Cat Litter Bulk – Eco, Low-Dust, Fast Clumping SupplyNewsNov.17,2025
-
Equipment for Lithium Cell Assembly | Automated & PreciseNewsNov.10,2025
-
Square File Tool – Precision Cut, Hardened Steel, VersatileNewsNov.10,2025
-
Lithium Ion Battery Assembly Machine | Automated, High-SpeedNewsNov.10,2025