Fast absorbing water inflation jute bag for flood control?
Jute Absorbing Water Inflation Bag: Field Notes, Specs, and Real-World Lessons
If you haven’t tried an absorbing water inflation jute bag for flood control yet, here’s why so many emergency crews are quietly switching. In fact, the shift from traditional sand-and-shovel to water-activated burlap is happening faster than most city buyers expected. You move fewer pallets, mobilize in minutes, and—this surprised me—jute holds up better than canvas after soaking.

Product snapshot and specs
Product name: Jute absorbing water inflation bag. Origin: Room 1410, No. 119 Zhongxing East Street, Xiangdu District, Xingtai City, Hebei Province, China.
| Parameter | Typical value (≈) |
|---|---|
| Type/Size | 40 × 60 cm |
| Outer fabric | Jute (burlap), high-permeability, flood-grade weave |
| Absorbent core | Water-swell polymer fill, sealed inner layer |
| Water uptake | ≈18–22 L per bag (real-world use may vary) |
| Swelling time | 3–7 minutes in fresh water; faster with agitation |
| Wet durability | Burlap outperforms canvas after soaking; better abrasion resistance |
| Shelf life (dry) | Up to 3 years sealed; store cool and dry |
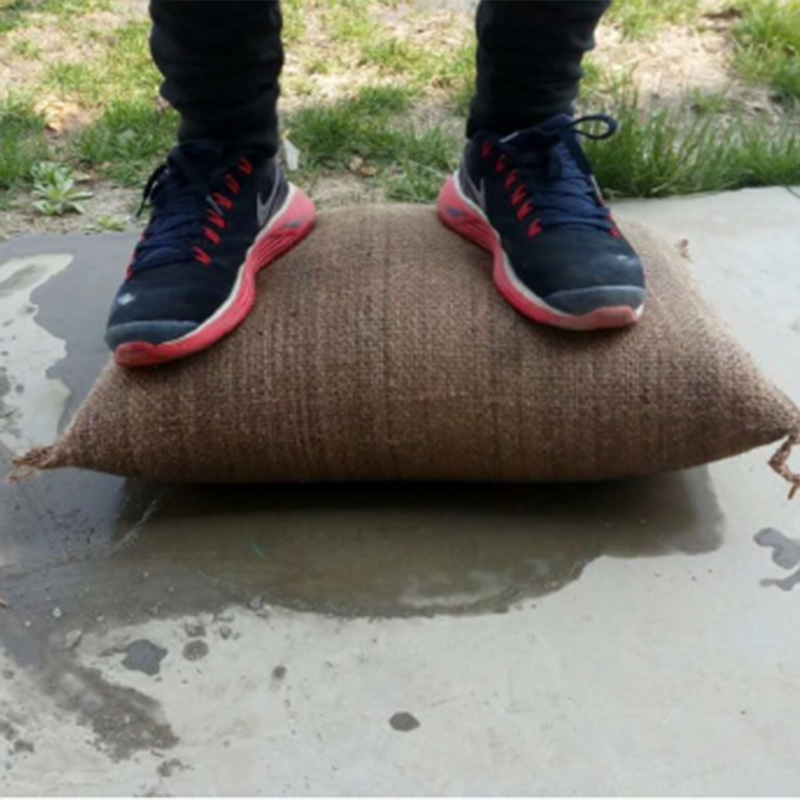

Why jute, why now?
Across municipalities and utility yards, the logistics math wins: one pallet of dry bags replaces multiple truckloads of sand. Jute’s permeability speeds water activation, and many customers say the grip feels “right” even when the bag is fully saturated. To be honest, I expected canvas to last longer—but after repeated wet cycles, burlap simply holds its weave better.
Process and testing
Materials are cut, overlock-stitched, and filled with a controlled polymer dose; seams are reinforced at stress points. Typical QA includes water-permeability checks (ASTM D4491 style), tensile testing on the jute shell (ISO 13934-1/ASTM D5035 methods), basic hydrostatic resistance (AATCC 127), and visual inspection after 30–60 min soak. Service window: deploy for hours to days; for semi-permanent berms, rotate fresh units as needed.

Use cases
- Doorways, garages, warehouse thresholds, and elevator shafts
- Rapid riverbank shoring and culvert overflow control
- Utilities: substation pads, manholes, telecom vaults
- Road crews: detours, shoulder washouts, quick cofferdams
How-to: soak 3–5 minutes or place where flow is present; stack in staggered brick pattern; tamp gently. Our absorbing water inflation jute bag for flood control typically reaches working density fast—good news when water’s already at the curb.
Vendor landscape (quick comparison)
| Vendor | Pros | Watch-outs |
|---|---|---|
| Shuoding (manufacturer) | Jute-first design; better wet abrasion; size 40×60 cm; customization; ISO-style QC | Lead time spikes in rainy season—pre-book |
| Generic importer | Low MOQs; mixed bundles | Variable polymer fill; inconsistent seams |
| Canvas alternatives | Tighter weave; neat finish | Slower water ingress; less durable after soaking |
Customization and compliance
Options: printed logos, color stitching, polymer load tuning (for faster/slower swell), UV additives, and carton/pallet configs. Common documentation: ISO 9001 factory QA, RoHS/REACH-SVHC screening for polymer contact materials (on request). Field data I’ve seen show 18–22 L uptake with ≈4–6% variance lot-to-lot—perfectly normal.

Mini case notes
- Coastal township, tidal surge: swapping 1,200 sandbags for 400 jute units cut setup time by ≈55%.
- Warehouse threshold kit: three layers of absorbing water inflation jute bag for flood control held back a 12 cm sheet flow; no pallet jack needed.
- Utility vaults: crews liked the hand-feel and said “stacking was easier than expected.”
Bottom line: if you need fast, clean deployment and prefer natural fibers over synthetics, a absorbing water inflation jute bag for flood control setup is hard to beat.
Contact/Origin: Room 1410, No. 119 Zhongxing East Street, Xiangdu District, Xingtai City, Hebei Province, China.
References
- USACE – Sandbagging Techniques (public guidance). https://www.spk.usace.army.mil/Portals/12/documents/emergency/sandbag.pdf
- ASTM D4491 – Water Permeability of Geotextiles by Permittivity (method reference). https://www.astm.org/d4491.html
- ISO 13934-1 – Textiles: Tensile properties of fabrics. https://www.iso.org/standard/61002.html
- ECHA – REACH Candidate List (SVHC). https://echa.europa.eu/candidate-list-table
Share
-
Lithium Battery Welding Machine | High-Precision, Fast, SafeNewsNov.17,2025
-
Aluminium Guide Roller | Anodized, Lightweight, Low-NoiseNewsNov.17,2025
-
Tofu Cat Litter Bulk – Eco, Low-Dust, Fast Clumping SupplyNewsNov.17,2025
-
Equipment for Lithium Cell Assembly | Automated & PreciseNewsNov.10,2025
-
Square File Tool – Precision Cut, Hardened Steel, VersatileNewsNov.10,2025
-
Lithium Ion Battery Assembly Machine | Automated, High-SpeedNewsNov.10,2025