Need a fast-cutting carbide rotary file for metal and drill?
Rotary File (Carbide Burrs): A Shop-Floor Insider’s Guide
If you cut, deburr, or blend hard metals for a living, you already know the quiet hero is the rotary file. In fact, it’s the thing that saves the shift when a burr sneaks in before finish, or when a radius needs finessing—right now. Below is a practical, non-glossy look at modern carbide burrs from Xingtai Shuoding (Hebei, China)—what’s changing, what’s worth your money, and what to spec when tolerance and uptime matter.
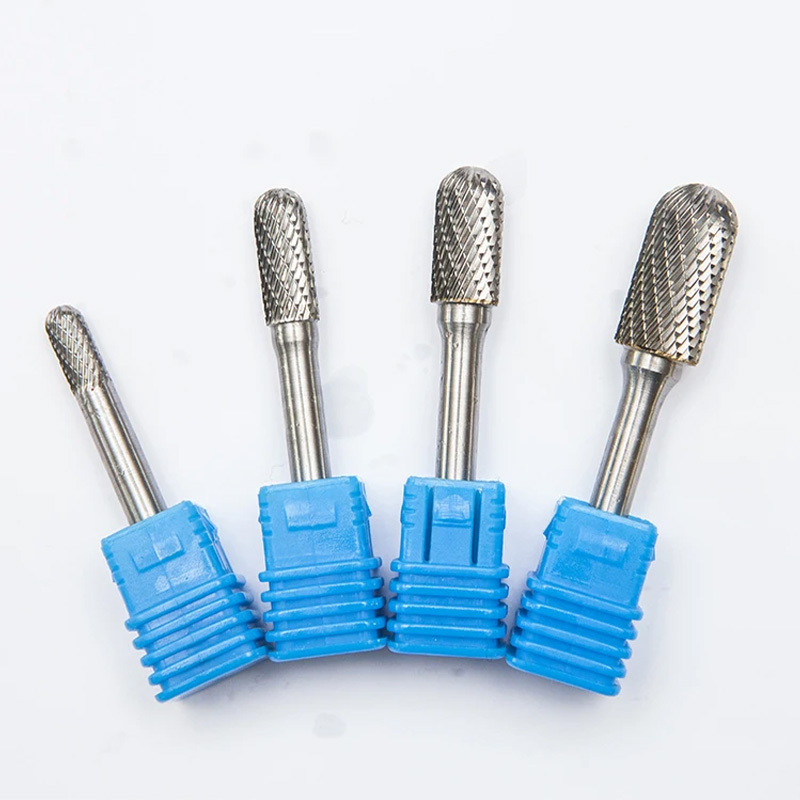

What it is and where it’s used
The rotary file—also called a carbide burr—is a small, brutally efficient cutter for deburring, shaping, grinding, and chamfering steels, cast iron, Inconel, titanium, and yes, aluminum (with the right flute). You’ll spot them in mold and die shops, aerospace repair cells, shipyards, automotive reman lines, and fabrication bays that live on real-world fixes, not just CAD ideals.
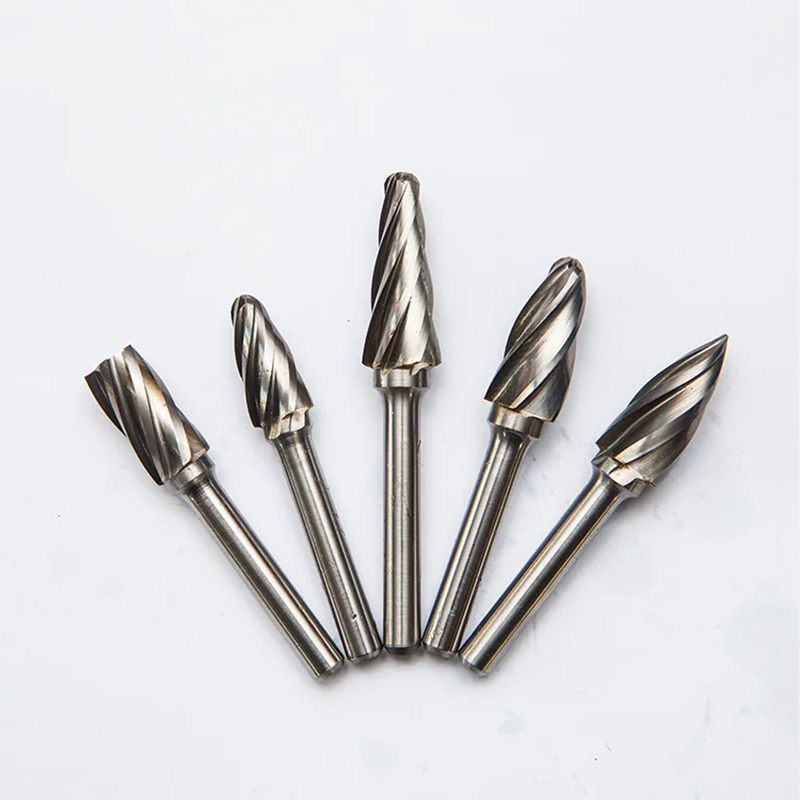

Industry trends (short version)
- Shift to fine‑grain K20–K25 carbide for longer life and less chipping on hard metals.
- Double-cut geometry for stainless and superalloys; aluminum-cut with big chip spaces for non-ferrous.
- Light coatings (TiAlN/AlTiN) for heat control; not always needed, but helpful on long stainless jobs.
- Better balancing and tighter runout (≤0.02 mm) to reduce chatter, which saves wrists and parts.
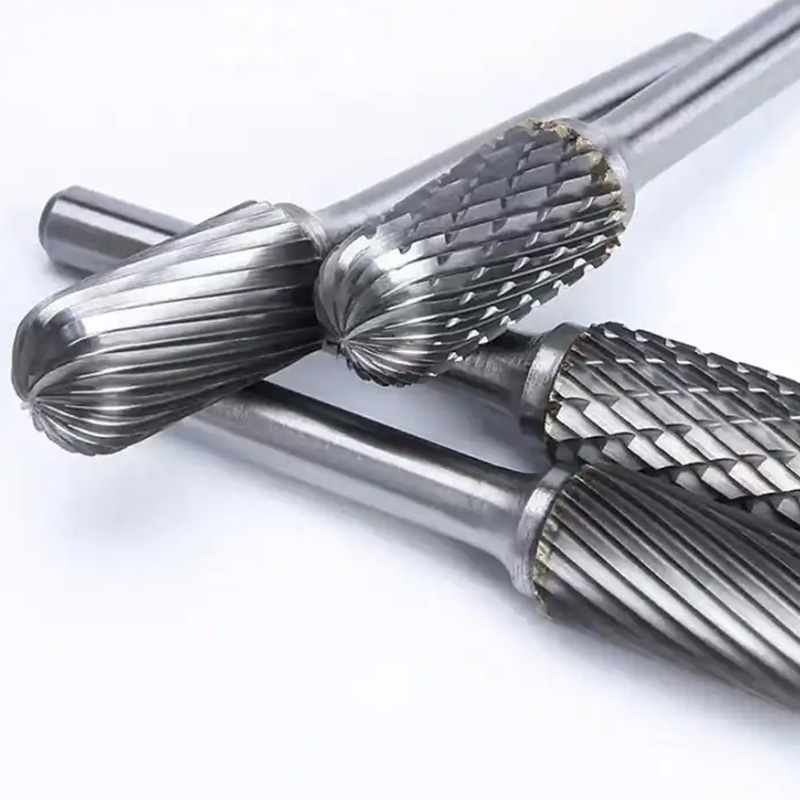
Process flow and build quality
Materials: fine‑grain tungsten carbide (≈ HRA 90–92) brazed or as solid carbide with hardened shanks. Methods: CNC flute grinding, edge-honing, dynamic balancing (down to G2.5 in many cases), ultrasonic cleaning, optional PVD coating. Testing: runout ≤0.02 mm at shank, torsion and brazing strength checks, visual inspection at 10×. Service life in the field varies—many customers say 2–5× HSS burr life on mild steel, around 1.5–3× on 304/316.

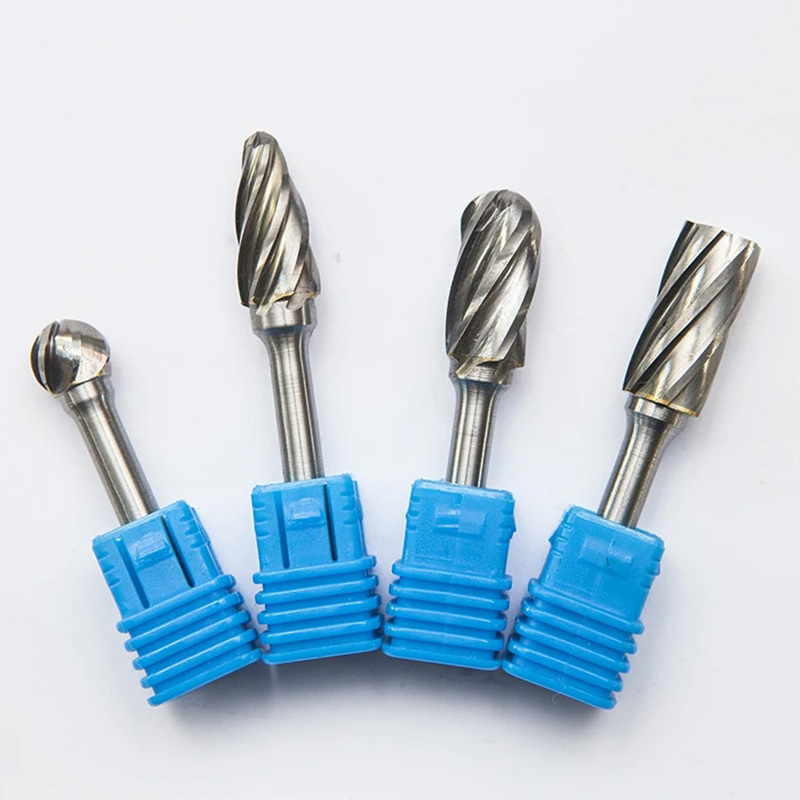
Product specifications (typical)
| Parameter | Spec (≈ / typical) |
|---|---|
| Carbide grade | K20–K25, fine‑grain |
| Shank diameters | 3 mm, 6 mm, 1/8", 1/4" |
| Shapes | Cylinder, ball, oval, tree, flame, cone, pointed |
| Cuts | Single, double, aluminum-cut, diamond-cut |
| Runout | ≤0.02 mm at shank |
| Recommended RPM | 10,000–35,000 (diameter-dependent) |
| Hardness | ≈ HRA 90–92 |
| Coatings | TiAlN/AlTiN optional |
Real-world performance (shop notes)
In our stainless test (304 plate, 6 mm double-cut burr, 20k RPM), average material removal hit ≈ 55–70 mm³/min with minimal loading. On 6061 with aluminum-cut, we saw ≈ 120–160 mm³/min. Not a lab in a white coat—just repeatable floor tests with a decent pneumatic grinder.

Vendor comparison (snapshot)
| Vendor | Carbide/Runout | Shapes/Cuts | Lead time | Customization | Certs |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Xingtai Shuoding | Fine-grain; ≤0.02 mm | Wide; single/double/AL-cut | 7–15 days typical | Shank, flute, engraving, kits | ISO 9001 |
| Generic off‑the‑shelf | Mixed; 0.03–0.05 mm | Standard only | Immediate | Limited | Varies |
Customization and sourcing
From Room 1410, No. 119 Zhongxing East Street, Xiangdu District, Xingtai City, Hebei Province, China, Shuoding offers custom shank diameters, special radii, unique flute counts, private labeling, and kit assortments. To be honest, the engraving option is handy in mixed-tool cribs.
Use cases and short wins
- Mold & die: gate removal and blend—cycle time down ≈18% in one customer trial.
- Shipbuilding: weld cap blending on HT steels—operators reported less chatter.
- Aerospace MRO: titanium edge breaks with single‑cut geometry—cleaner chip flow.
One buyer told me, “We swapped to double‑cut on 316 and stopped babying the grinder.” Not scientific, but you hear it a lot.
Safety, speeds, and good habits
Keep RPM within the diameter chart, avoid side load on long-reach burrs, and use eye/respiratory protection. Debris from double-cut can be fine—capture it. Actually, a light touch extends life more than any coating trick.
Certifications and standards referenced
Built under ISO 9001 systems; geometry and shanks aligned to DIN‑series burr standards; material selection per ISO tooling guidance; balancing practices referenced to ISO 21940 where applicable.
Authoritative citations
Share
-
Lithium Battery Welding Machine | High-Precision, Fast, SafeNewsNov.17,2025
-
Aluminium Guide Roller | Anodized, Lightweight, Low-NoiseNewsNov.17,2025
-
Tofu Cat Litter Bulk – Eco, Low-Dust, Fast Clumping SupplyNewsNov.17,2025
-
Equipment for Lithium Cell Assembly | Automated & PreciseNewsNov.10,2025
-
Square File Tool – Precision Cut, Hardened Steel, VersatileNewsNov.10,2025
-
Lithium Ion Battery Assembly Machine | Automated, High-SpeedNewsNov.10,2025