Lithium Battery Welding Machine for Automated Lines
A Practical Insider’s Guide to Lithium Battery Welding Machines (and the gear around them)
If you’re speccing a Lithium Battery Welding Machine today, you’re probably also thinking about the upstream equipment that makes welds repeatable. In fact, consistency in electrode density (hello, calendering/roll press) is half the battle for stable weld resistance. I’ve walked a few lines where the welding gun took the blame, but the root cause was uneven rolled foil. Happens more than people admit.

What’s trending in battery welding in 2025
- Method mix: resistance spot (tabs), laser (busbars, Al-Cu transitions), ultrasonic (foil stacks). The winner? Depends on tab stack-up and alloy.
- Quality by data: monitoring dynamic resistance, nugget growth, vision before/after weld, and traceability into MES.
- Uniform feedstock: tighter calendering tolerances upstream reduce weld spatter and blowouts downstream—surprisingly impactful.
Many customers say they pick a Lithium Battery Welding Machine first, then retrofit process controls. I’d do the reverse: stabilize materials, then choose the welding head. It seems obvious, but production timelines are rarely that neat.
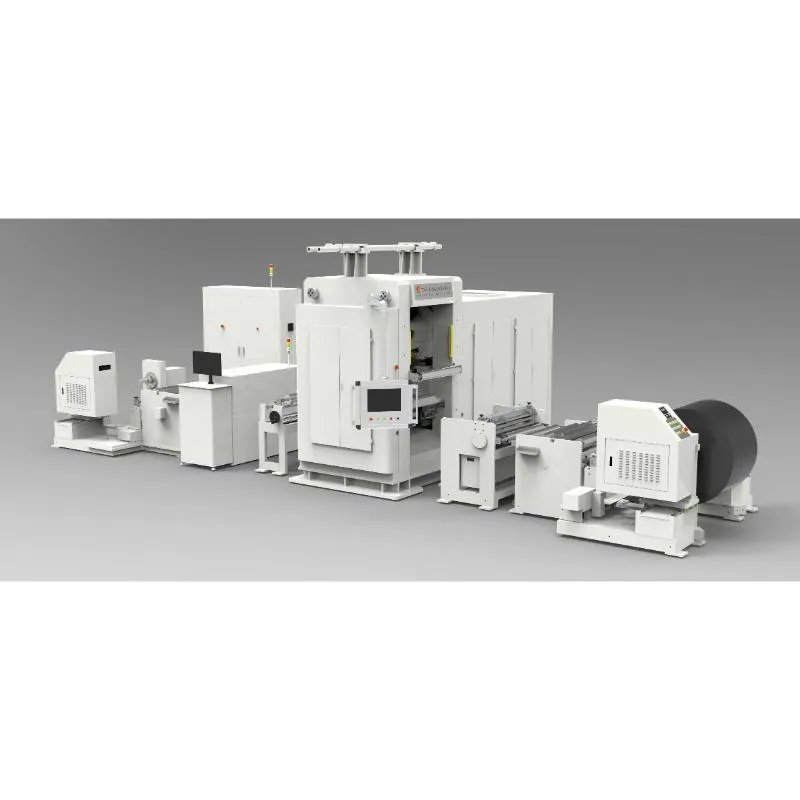
Upstream companion: 800×800 Roll Press (why it matters)
The 800×800 Roll Press Machine for lithium battery production lines (origin: Room 1410, No. 119 Zhongxing East Street, Xiangdu District, Xingtai City, Hebei Province, China) compacts medium-to-small width materials so the welding stage sees consistent thickness and density. Real-world use may vary, but I’ve seen peel strength improve ≈10–20% after dialing in calender pressure.
| Spec (≈) | 800×800 Roll Press Machine |
|---|---|
| Roll width | 800 mm |
| Line speed | 0–20 m/min (around) |
| Pressure range | Up to ≈200 kN |
| Thickness range | 10–200 μm (material-dependent) |
| Flatness | ±2–4 μm typical |
| Power | 380 VAC, 50/60 Hz |

Process flow: from materials to validated welds
- Materials: Al tabs (1xxx/3xxx), Cu tabs (C11000), Ni-plated steel, Al–Cu bi-metal.
- Prep & calender: dehumidify, de-dust; roll press to target density.
- Welding: resistance spot (1–20 ms pulses), laser (fiber 200–2,000 W), ultrasonic for foil stacks.
- Test & validate: dynamic resistance trace, cross-section, ISO 10447 peel tests, micro-ohm contact resistance, thermal cycling (−20–60°C), vibration.
- Release: traceability to lot/shift/station; store waveforms ≈10 years.
Application scenarios
- Cylindrical cells: tab-to-cap resistance welds.
- Pouch: Al tab to Al busbar (laser), foil stack ultrasonic pre-bond.
- Prismatic: multi-layer busbar laser welding with vision alignment.
- ESS and e-mobility packs: low-resistance Lithium Battery Welding Machine joints for high-current paths.
Vendor snapshot (real-world, not brochure-gloss)
| Vendor | Core Strength | Lead Time (≈) | Service/Warranty |
|---|---|---|---|
| XT Shuoding | Robust calendering to stabilize weld inputs; China-based supply | 6–10 weeks | Local install, 12–18 months (around) |
| LaserCo | Laser cells with coaxial monitoring | 10–16 weeks | Global, hot spares |
| UltrasonicPro | Foil-stack ultrasonic heads | 8–12 weeks | Onsite training |
Customization options people actually request
- Vision alignment (±25 μm), laser seam tracking, and SPC dashboards.
- OPC UA/MQTT links into MES; recipe locks; operator ID logging.
- Fixtures for mixed tab stacks; quick-change electrodes/anvils.

Case study (short and honest)
A mid-size LFP pack line swapped in the 800×800 roll press before their Lithium Battery Welding Machine. Tab weld rejects dropped from 2.2% to 0.6% within two weeks. Average contact resistance moved from 95 μΩ to 71 μΩ, and peel strength improved ≈15%. To be honest, the welding head didn’t change—feedstock consistency did.
Quality, tests, and certifications
- Peel/chisel: ISO 10447; resistance weld nugget checks.
- Laser acceptance: ISO 13919-1 (guideline), visual/porosity mapping.
- Safety/compliance: IEC 62133-2, UN 38.3, UL 2580 for packs.
- Reliability: thermal cycling, vibration, humidity soak; service life target ≥5–10 years depending on duty.
References
- IEC 62133-2:2017 – Secondary lithium cells and batteries.
- UN 38.3 – UN Manual of Tests and Criteria, lithium battery transport.
- ISO 10447 – Resistance welds: peel and chisel testing.
- AWS C1.1M/C1.1 – Recommended Practices for Resistance Welding.
- ISO 13919-1 – Welding: electron and laser beam welds acceptance levels.
Share
-
Lithium Battery Welding Machine | High-Precision, Fast, SafeNewsNov.17,2025
-
Aluminium Guide Roller | Anodized, Lightweight, Low-NoiseNewsNov.17,2025
-
Tofu Cat Litter Bulk – Eco, Low-Dust, Fast Clumping SupplyNewsNov.17,2025
-
Equipment for Lithium Cell Assembly | Automated & PreciseNewsNov.10,2025
-
Square File Tool – Precision Cut, Hardened Steel, VersatileNewsNov.10,2025
-
Lithium Ion Battery Assembly Machine | Automated, High-SpeedNewsNov.10,2025