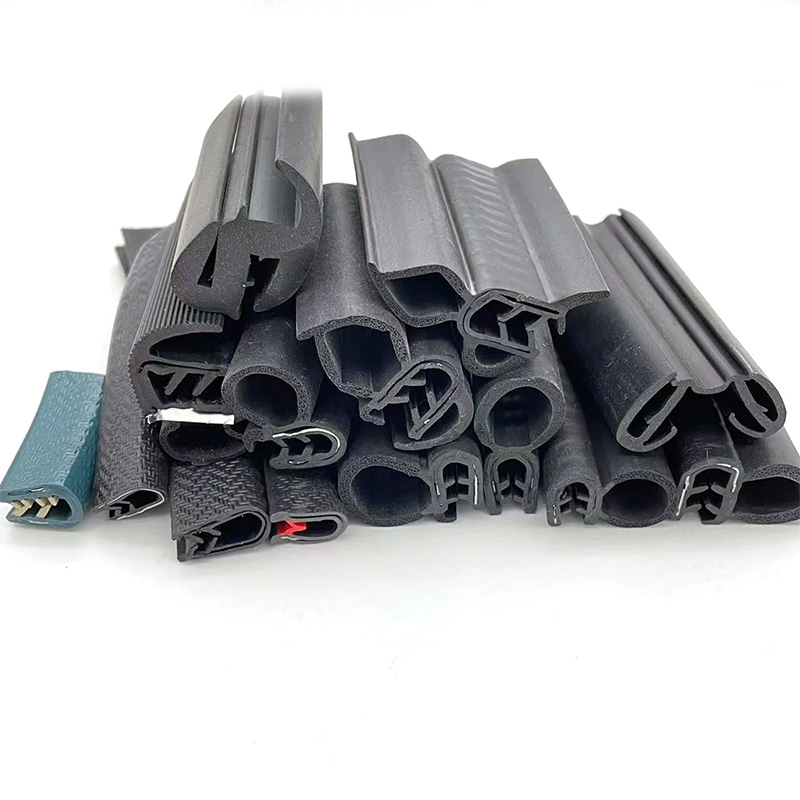
D Type Rubber Door Seal: Premium Sound & Weatherproof Protection
Industry Trends and the Critical Role of Sealing Solutions
The demand for high-performance sealing solutions in industrial and commercial sectors continues to surge, driven by stringent energy efficiency regulations, the need for enhanced operational safety, and the increasing complexity of environmental protection standards. Within this evolving landscape, the d type rubber door seal has emerged as a cornerstone component, pivotal in achieving optimal thermal, acoustic, and particulate containment. Modern industrial applications, from advanced manufacturing facilities to critical infrastructure projects, are increasingly adopting specialized sealing profiles like the D-type due to their superior compression set resistance, broad temperature stability, and chemical inertness. The market is witnessing a trend towards materials offering extended service life and customized properties, such as enhanced UV resistance for outdoor applications or fire retardancy for safety-critical environments.
Relatedly, the evolution of door edge rubber seal and door frame rubber seal technologies is directly influenced by advancements in polymer science. Innovations in composite materials, particularly those combining the benefits of silicone, EVA, and CR rubber foam, are enabling the creation of seals that offer unprecedented performance. This includes improved elasticity for better conformability, superior recovery characteristics under sustained compression, and a wider operational temperature range. For instance, in the petrochemical industry, the demand for seals resistant to aggressive hydrocarbons and extreme temperatures is paramount. Similarly, in high-precision manufacturing, a reliable door frame rubber seal strip ensures controlled environments, minimizing dust ingress and maintaining air purity. These trends underscore the critical need for expertly engineered sealing solutions that not only meet but exceed contemporary industrial requirements.

Manufacturing Process of a D Type Rubber Door Seal
The production of a high-quality d type rubber door seal is a sophisticated process involving several key stages, from material selection to final quality control. This intricate manufacturing flow ensures that the end product meets the rigorous performance specifications required by various industries.
Detailed Process Flow:
-
Material Preparation & Compounding:
This initial stage is critical. Raw polymers such as Silicone (for high-temperature resistance and environmental stability), Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA, for flexibility and shock absorption), and Chloroprene Rubber (CR, also known as Neoprene, for excellent oil, chemical, and weather resistance) are selected based on the desired application. These base materials, often in foam sheet forms, are mixed with various additives including curing agents (vulcanizing agents), accelerators, activators, fillers (e.g., carbon black for strength, silica for translucency), plasticizers, and anti-degradants. This compounding process is performed in Banbury mixers or two-roll mills to create a homogenous rubber compound with specific physical and chemical properties. The precise formulation dictates the seal's hardness (Shore A), tensile strength, elongation at break, and chemical resistance.
-
Extrusion:
Once compounded, the rubber material is fed into an extruder. Under high pressure and controlled temperature, the material is forced through a die plate, which is precisely shaped to form the characteristic "D" profile of the rubber seal. This process, analogous to continuous casting for metals but adapted for polymers, creates a continuous length of the D-type rubber seal. The consistency of the extrusion pressure and temperature is paramount to maintain dimensional accuracy and surface finish.
-
Vulcanization (Curing):
After extrusion, the un-vulcanized (green) rubber profile enters a continuous vulcanization line, often using hot air ovens, salt baths, or microwave systems. Vulcanization is a chemical process that cross-links the polymer chains, transforming the rubber from a plastic, deformable state into an elastic, durable material. This significantly enhances the seal's mechanical properties, including its tensile strength, tear resistance, compression set, and overall service life. The exact temperature and duration of curing are critical and specific to the polymer blend.
-
Cooling & Sizing:
The cured rubber profile is then cooled, typically with water or air, to stabilize its dimensions and prevent distortion. During this stage, precision cutting equipment trims the continuous profile into specific lengths as per customer requirements or standard specifications. CNC machining is often employed here for highly accurate length cuts or for creating specific end-finishes for intricate door frame rubber seal designs.
-
Surface Treatment & Finishing:
Depending on the application, seals may undergo additional surface treatments. This can include applying flocking for reduced friction and improved aesthetic, or anti-tack coatings to prevent sticking. For specialized door edge rubber seal applications, adhesive backing might be applied.
-
Quality Control & Testing:
Every batch of seals undergoes rigorous testing to ensure compliance with international standards such as ISO 3302-1 (Dimensional Tolerances), ASTM D2240 (Hardness), ASTM D412 (Tensile Strength & Elongation), and ASTM D395 (Compression Set). Additional tests may include ozone resistance (ASTM D1149), fluid resistance, temperature cycling, and accelerated aging tests. For critical applications, seals may also be tested against ANSI standards for specific industries like HVAC or fire safety regulations.
The target industries for these seals are diverse, including petrochemical (for sealing access panels and control cabinet doors against aggressive chemicals), metallurgy (withstanding high temperatures and abrasive dust), and water supply & drainage (ensuring watertight seals in critical infrastructure). Advantages in typical application scenarios include significant energy saving by preventing air infiltration and exfiltration, superior corrosion resistance due to material inertness, and extended service life due to excellent mechanical properties.

Technical Specifications and Performance Parameters
Understanding the technical specifications of a d type rubber door seal is crucial for engineers and procurement professionals to ensure optimal performance in demanding B2B environments. These parameters dictate the seal's suitability for specific operational conditions and expected service life.
Typical Product Specifications (Based on Silicone/EVA/CR Blends):
| Parameter | Description | Typical Value Range | Relevant Standard |
|---|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Silicone, EVA, CR (Neoprene) Foam Blends | Varies by formulation | ASTM D2000 Classification |
| Hardness (Shore A) | Resistance to indentation | 20-70 Shore A | ASTM D2240 |
| Tensile Strength | Stress at break | 5-15 MPa (725-2175 psi) | ASTM D412 |
| Elongation at Break | Percentage increase in length before breaking | 200-700% | ASTM D412 |
| Compression Set (22h @ 70°C) | Permanent deformation after compression | < 25% | ASTM D395, Method B |
| Operating Temperature Range | Min/Max temperatures for functional use | -60°C to +200°C (-76°F to +392°F) | ISO 11844 |
| Water Absorption | Percentage weight gain after immersion | < 3% | ASTM D471 |
| Ozone Resistance | Resistance to cracking/degradation from ozone | Excellent | ASTM D1149 |
| Flame Retardancy | Ability to resist flame spread | UL94 V-0 (Self-extinguishing) option | UL94, NFPA 130 |
These specifications highlight the robust engineering behind a quality d type rubber seal, offering predictable performance under diverse conditions. The foam sheet base materials contribute to properties like excellent thermal insulation and acoustic dampening, critical for energy efficiency and noise reduction in industrial settings. Custom formulations can be developed to meet even more specific requirements, ensuring optimal sealing integrity.

Application Scenarios and Technical Advantages
The versatility of the d type rubber door seal makes it an indispensable component across numerous B2B sectors. Its unique profile and material composition offer significant technical advantages that translate directly into operational efficiencies and cost savings for businesses.
Typical Application Scenarios:
- Industrial Enclosures and Cabinets: Critical for sealing electrical enclosures, control panels, and outdoor equipment cabinets against dust, moisture (IP ratings), and temperature fluctuations. The door frame rubber seal strip ensures protection of sensitive electronics and machinery.
- HVAC Systems: Used in air handling units, ventilation ducts, and cleanroom access doors to prevent air leakage, thereby enhancing energy efficiency and maintaining precise environmental control.
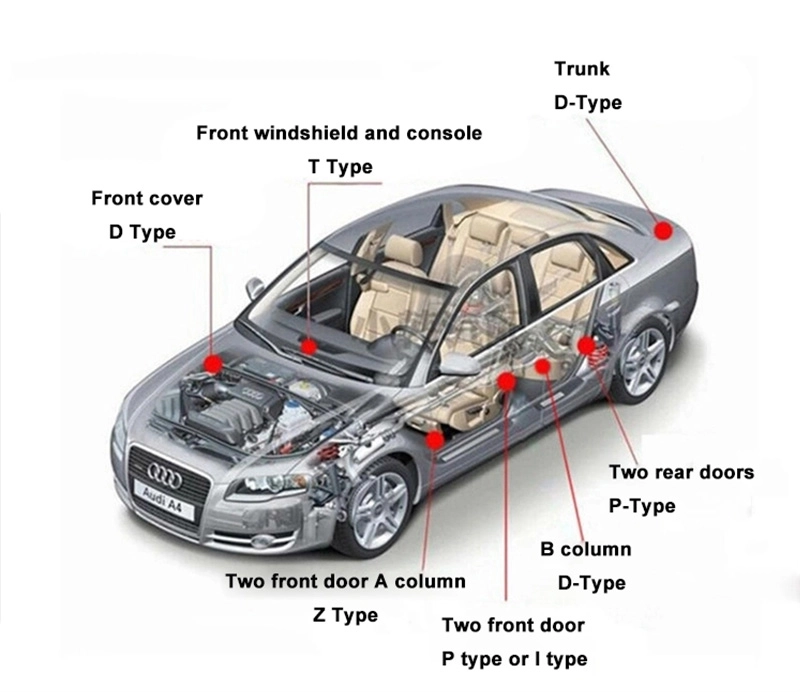
- Automotive and Transportation: Applied in vehicle doors, trunks, and windows to provide weather sealing, reduce noise, and minimize vibrations. The durability of the rubber seal withstands constant movement and exposure to road conditions.
- Construction and Architecture: Integrated into commercial building doors, windows, and curtain wall systems for superior thermal insulation, soundproofing, and weatherproofing. A robust door edge rubber seal can significantly impact building performance.
- Marine Applications: Essential for sealing watertight doors, hatches, and portholes on vessels, resisting saltwater corrosion, UV radiation, and extreme weather conditions.
- Food Processing and Pharmaceutical Facilities: Used in hygienic environments for sealing doors of ovens, freezers, and cleanrooms, often requiring FDA-compliant materials for non-toxic and easy-to-clean properties.
Key Technical Advantages:
- Superior Sealing Integrity: The D-profile design, with its hollow or solid core, offers excellent compression and recovery characteristics, ensuring a consistent and tight seal even after prolonged periods of compression. This prevents ingress of dust, water, air, and pollutants.
- Energy Efficiency: By minimizing air leakage and providing thermal insulation, these seals contribute significantly to energy saving in heated or cooled environments. This is particularly crucial in facilities with large energy footprints like data centers and cold storage units.
- Enhanced Durability and Service Life: Formulations incorporating Silicone, EVA, and CR rubber foam offer exceptional resistance to aging, UV radiation, ozone, and a broad range of chemicals and solvents. This translates to reduced maintenance and replacement costs.
- Vibration and Noise Dampening: The elastic properties of the rubber and the D-profile act as effective shock absorbers, reducing vibration transmission and attenuating noise, thereby improving working conditions and equipment longevity.
- Corrosion Resistance: For applications in corrosive environments (e.g., petrochemical, marine), the inherent chemical resistance of specialized rubber compounds protects underlying metal structures from degradation.
- Temperature Stability: Capable of performing reliably across extreme temperature ranges, from sub-zero conditions in cold storage to high temperatures in industrial ovens, ensuring consistent sealing performance.

Vendor Comparison and Customized Solutions
Choosing the right supplier for d type rubber seal products is critical for long-term project success. B2B decision-makers must consider not only standard product offerings but also the capability for customized solutions, technical support, and vendor reliability.
Key Vendor Comparison Factors:
| Factor | Premium Vendor (e.g., XT Shuoding) | Standard Vendor |
|---|---|---|
| Material Expertise | Specialized in Silicone, EVA, CR foam, custom blends for specific chemical/thermal resistance. Offers FDA/UL certified materials. | Standard EPDM, PVC, limited material options. |
| Customization Capabilities | Full R&D support for custom profiles, dimensions, material formulations, colors, and adhesive backing options. Engineering consultation available. | Limited to existing dies and standard profiles. Minimal material alteration. |
| Quality Certifications | ISO 9001, IATF 16949 (for automotive), RoHS, REACH compliance. Provides full batch traceability and test reports. | Basic quality control, may lack specific industry certifications. |
| Technical Support | Dedicated engineering team, application support, failure analysis, and ongoing product development assistance. | Limited post-sales support, primarily order fulfillment. |
| Lead Time & Reliability | Optimized production cycles, robust supply chain, and high on-time delivery rates. Inventory management solutions. | Variable lead times, potential for supply chain disruptions, standard order processing. |
| Cost vs. Value | Higher initial cost, but significantly lower total cost of ownership (TCO) due to extended lifespan, superior performance, and reduced failures. | Lower initial cost, but potentially higher TCO from frequent replacements, performance compromises, and operational downtime. |
Customized Solutions: Tailoring the D Type Rubber Seal to Your Needs
The efficacy of a door frame rubber seal or a door edge rubber seal often hinges on its precise fit and material compatibility with the application environment. Recognizing this, leading manufacturers offer extensive customization options:
- Profile and Dimensions: Beyond standard D-profiles, custom cross-sections, wall thicknesses, and hollow/solid configurations can be engineered to optimize compression force, sealing area, and installation methods.
- Material Formulations: Adjustments to the blend of Silicone, EVA, and CR rubber foam, or the addition of other polymers and additives, can fine-tune properties such as hardness, chemical resistance, temperature range, UV stability, and flame retardancy (e.g., meeting UL94 V-0 requirements).
- Color Matching: For aesthetic or coding purposes, seals can be produced in specific colors to match equipment or designate function.
- Adhesive Backing: Application-specific adhesive systems (e.g., acrylic, rubber-based, heat-activated) can be pre-applied for ease of installation and secure adhesion to various substrates, critical for door frame rubber seal strip applications.
- Special Features: This includes incorporating drain channels, anti-friction coatings, or conductive properties for EMI/RFI shielding, expanding the functional utility of the rubber seal.
Engaging with a vendor capable of such comprehensive customization ensures that the final d type rubber door seal is perfectly optimized for the application, maximizing performance and delivering superior return on investment.

Application Case Studies and Customer Success
Case Study 1: Energy Sector - Petrochemical Plant Control Room
A major petrochemical complex faced significant challenges with maintaining stable environmental conditions within their central control rooms. Existing door seals were degrading rapidly due to exposure to trace corrosive fumes, high humidity, and frequent temperature fluctuations. This led to increased energy consumption for HVAC systems and potential ingress of dust and harmful gases, posing risks to sensitive electronics and personnel safety.
- Solution: We provided a custom-engineered d type rubber door seal fabricated from a specialized CR (Neoprene) and Silicone blend. This formulation offered enhanced chemical resistance, superior ozone and UV stability, and an extended operating temperature range. The D-profile was optimized for the specific door clearances, and an aggressive, pressure-sensitive adhesive backing was incorporated for robust attachment.
- Results: Post-installation, the plant reported a measurable 15% reduction in HVAC energy consumption in the sealed areas. Air quality monitoring showed a significant decrease in particulate and fume ingress. The seals have demonstrated exceptional longevity, exceeding the service life of previous solutions by over 50%, with no visible signs of degradation after three years of continuous operation. The client praised the proactive technical support and the seamless integration process.
Case Study 2: High-Tech Manufacturing - Cleanroom Access Doors
A leading semiconductor fabrication facility required an upgrade to their cleanroom access door sealing systems. The existing seals were failing to consistently maintain ISO Class 5 cleanroom standards, leading to product contamination risks and increased operational costs due to rework and scrap. The critical requirement was a seal that offered ultra-low particle shedding, excellent compression set, and consistent air-tightness.
- Solution: We developed a bespoke door frame rubber seal strip using medical-grade, platinum-cured Silicone foam, known for its inertness, low outgassing, and excellent elasticity. The D-type profile was designed with a specific hollow core to provide optimal compression characteristics, ensuring a perfect seal with minimal force. The seals were manufactured in a controlled environment to minimize contamination during production.
- Results: The new d type rubber seal drastically improved the cleanroom's sealing performance, maintaining consistent pressure differentials and reducing particle counts well within ISO Class 5 requirements. The facility experienced a significant reduction in product contamination rates, leading to improved yield and substantial cost savings. The ease of installation, coupled with the long-term reliability of the Silicone seals, received positive feedback from the maintenance team.
Case Study 3: Commercial Building Management - Acoustic and Thermal Sealing
A prominent commercial high-rise in a bustling urban center aimed to enhance occupant comfort by improving acoustic insulation and thermal performance for all exterior-facing doors. Standard EPDM door edge rubber seal solutions were insufficient in mitigating street noise and preventing heat transfer, leading to complaints and higher utility bills.
- Solution: Our team recommended and supplied a series of D-type door frame rubber seal solutions utilizing an advanced EVA/CR foam blend. This material provided excellent acoustic dampening properties and superior thermal insulation compared to conventional rubber. The seals were precisely sized and provided with a strong, weather-resistant adhesive for secure outdoor installation.
- Results: Post-implementation, the building management reported a noticeable improvement in interior acoustics, with street noise levels significantly reduced. Thermal imaging confirmed a substantial reduction in heat loss/gain around door perimeters, contributing to an estimated 10-12% reduction in heating and cooling costs. Tenant satisfaction improved, and the aesthetic integration of the clean-looking seals was also highlighted as a positive.
Trustworthiness: FAQ, Lead Time, Warranty, and Support
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
-
Q: What is the typical service life of a d type rubber door seal?
A: The service life varies significantly based on material, application environment (temperature, UV exposure, chemical contact), and frequency of compression. Generally, our high-grade Silicone/EVA/CR blends offer an estimated service life of 5-15 years in typical industrial conditions, often exceeding 20 years in less severe applications.
-
Q: Can these seals withstand extreme temperatures?
A: Yes, our specialized formulations, particularly those with a high Silicone content, are designed to operate effectively in a broad temperature range, typically from -60°C to +200°C (-76°F to +392°F). Specific material choices will optimize performance for your exact temperature profile.
-
Q: Are your products compliant with industry standards?
A: Absolutely. Our manufacturing processes and products adhere to stringent international standards, including ISO 9001 for quality management. Materials can be supplied to meet specific industry requirements such as ASTM, UL94, FDA, RoHS, and REACH compliance, depending on the application.
-
Q: How do I select the right D-type profile and material for my application?
A: We recommend consulting with our engineering team. Provide details on your application environment (temperature, chemicals, UV exposure), desired compression force, gap dimensions, and any specific performance requirements (e.g., soundproofing, fire resistance). Our experts will guide you to the optimal solution.
Lead Time and Fulfillment Details
We understand the critical importance of timely delivery in B2B operations. Our standard lead time for off-the-shelf d type rubber seal products is typically 2-4 weeks, subject to order volume. For custom-engineered solutions, the lead time will vary based on design complexity, tooling requirements, and material availability, with an estimated range of 6-12 weeks from finalized design to delivery. We maintain robust inventory management and an efficient logistics network to ensure reliable fulfillment. Expedited services are available for urgent projects upon request.
Warranty Commitments
We stand behind the quality and performance of our products. All our d type rubber door seal products are covered by a comprehensive warranty against manufacturing defects and material failures under normal operating conditions. The standard warranty period is 12 months from the date of purchase. Extended warranty options are available for specific long-term projects or critical applications, providing our clients with peace of mind and assurance of product reliability.
Customer Support and After-Sales Service
Our commitment to our clients extends far beyond product delivery. We offer dedicated customer support through a team of experienced technical professionals ready to assist with installation guidance, troubleshooting, and ongoing performance optimization. Our after-sales service includes product training, on-site technical assistance for complex installations, and a responsive query resolution system. We believe in building long-term partnerships, ensuring that our door frame rubber seal and door edge rubber seal solutions continue to meet your evolving operational needs.
References
- ISO. (2018). ISO 3302-1: Rubber - Tolerances for products - Part 1: Dimensional tolerances. International Organization for Standardization.
- ASTM International. (2020). ASTM D2240: Standard Test Method for Rubber Property—Durometer Hardness. ASTM International.
- ASTM International. (2021). ASTM D412: Standard Test Methods for Vulcanized Rubber and Thermoplastic Elastomers—Tension. ASTM International.
- ASTM International. (2018). ASTM D395: Standard Test Methods for Rubber Property—Compression Set. ASTM International.
- Underwriters Laboratories. (2020). UL 94: Tests for Flammability of Plastic Materials for Parts in Devices and Appliances. Underwriters Laboratories Inc.
Share
-
Lithium Battery Welding Machine | High-Precision, Fast, SafeNewsNov.17,2025
-
Aluminium Guide Roller | Anodized, Lightweight, Low-NoiseNewsNov.17,2025
-
Tofu Cat Litter Bulk – Eco, Low-Dust, Fast Clumping SupplyNewsNov.17,2025
-
Equipment for Lithium Cell Assembly | Automated & PreciseNewsNov.10,2025
-
Square File Tool – Precision Cut, Hardened Steel, VersatileNewsNov.10,2025
-
Lithium Ion Battery Assembly Machine | Automated, High-SpeedNewsNov.10,2025