Equipment For Lithium Cell Assembly
Introduction:
The assembly of lithium cells requires a meticulous selection of equipment to ensure efficiency, safety, and quality. From electrode coating to cell sealing, each stage demands specialized tools and machinery to streamline the process. In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the essential equipment for lithium cell assembly, providing detailed insights into their functionalities and importance.
Coating Equipment:
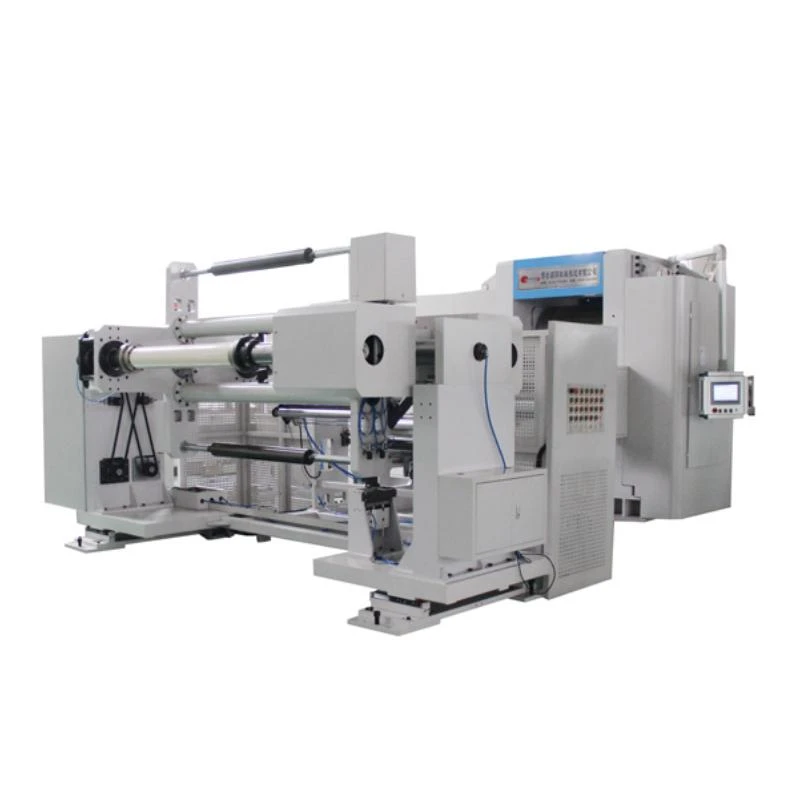
The electrode coating stage is critical in determining the performance and longevity of lithium cells. Coating machines, such as roll-to-roll coaters and slot die coaters, facilitate uniform application of electrode materials onto substrates. Precision control systems ensure consistent thickness and distribution, optimizing cell performance. Additionally, drying ovens and calendaring machines are indispensable for achieving desired electrode characteristics, enhancing conductivity and adhesion.
Assembly Line Automation:
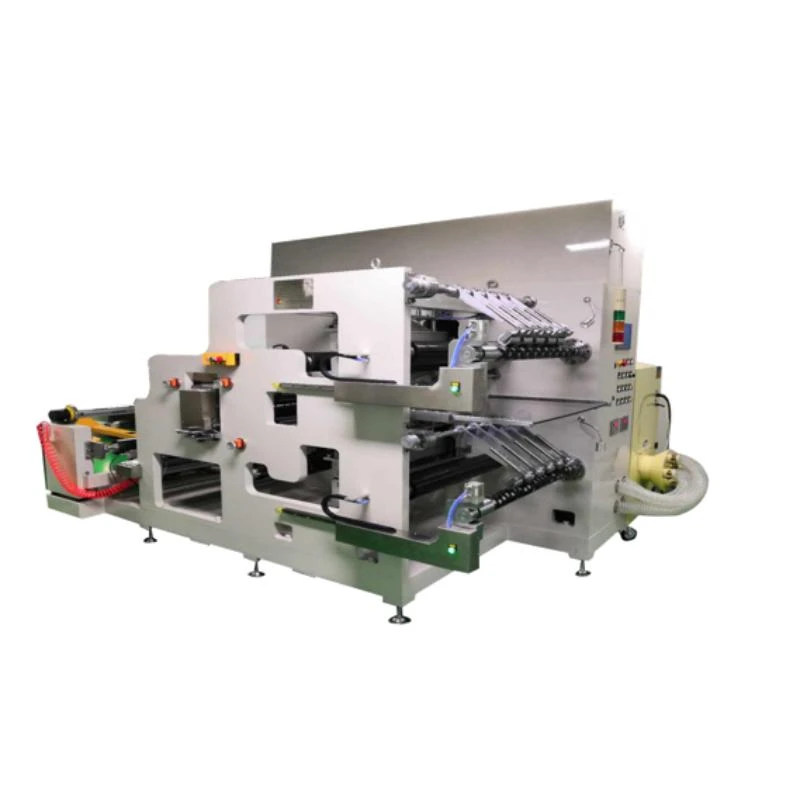
Efficient assembly line automation is paramount in mass production of lithium cells. Robotic arms equipped with grippers and vision systems enable high-speed handling and positioning of components. Conveyor systems ensure seamless transfer between assembly stations, minimizing downtime and increasing throughput. Advanced control software orchestrates the entire process, allowing for real-time monitoring and adjustment to maintain quality standards.
Electrolyte Filling Systems:
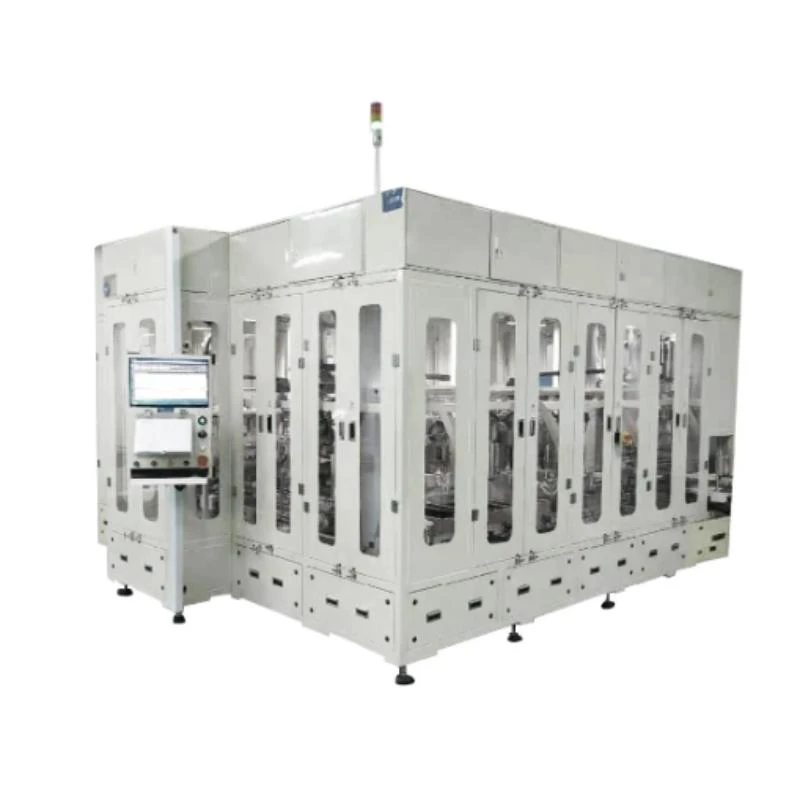
The accurate filling of electrolyte is crucial to the functionality and safety of lithium cells. Automated dispensing systems precisely meter electrolyte volumes into cell compartments, minimizing variations and ensuring consistency. Vacuum sealing machines then securely seal the cells, preventing leakage and contamination. Inert atmosphere glove boxes provide a controlled environment, eliminating moisture and oxygen exposure during filling and sealing processes.
Formation and Testing Equipment:
Formation and testing equipment validate the performance and reliability of lithium cells before distribution. Formation chambers subject cells to specific charge and discharge cycles, conditioning them for optimal capacity and stability. Integrated monitoring systems track key parameters such as voltage, current, and temperature, ensuring compliance with industry standards. In-line testing stations conduct rigorous quality assessments, identifying defects and outliers for further analysis.
Safety Measures:
Safety remains a paramount concern throughout the lithium cell assembly process. Fire suppression systems equipped with sensors and extinguishing agents mitigate the risk of thermal runaway events. Emergency shutdown protocols and containment measures are in place to prevent potential hazards. Personal protective equipment, including gloves, goggles, and fire-resistant clothing, is mandatory for personnel working in proximity to assembly lines.
Conclusion:
The assembly of lithium cells relies on a diverse range of equipment tailored to each stage of the manufacturing process. From electrode coating to final testing, precision machinery and automation systems ensure efficiency, quality, and safety. By investing in advanced equipment and adhering to stringent protocols, manufacturers can meet the growing demand for reliable and high-performance lithium battery solutions.
Share
-
Lithium Battery Welding Machine | High-Precision, Fast, SafeNewsNov.17,2025
-
Aluminium Guide Roller | Anodized, Lightweight, Low-NoiseNewsNov.17,2025
-
Tofu Cat Litter Bulk – Eco, Low-Dust, Fast Clumping SupplyNewsNov.17,2025
-
Equipment for Lithium Cell Assembly | Automated & PreciseNewsNov.10,2025
-
Square File Tool – Precision Cut, Hardened Steel, VersatileNewsNov.10,2025
-
Lithium Ion Battery Assembly Machine | Automated, High-SpeedNewsNov.10,2025