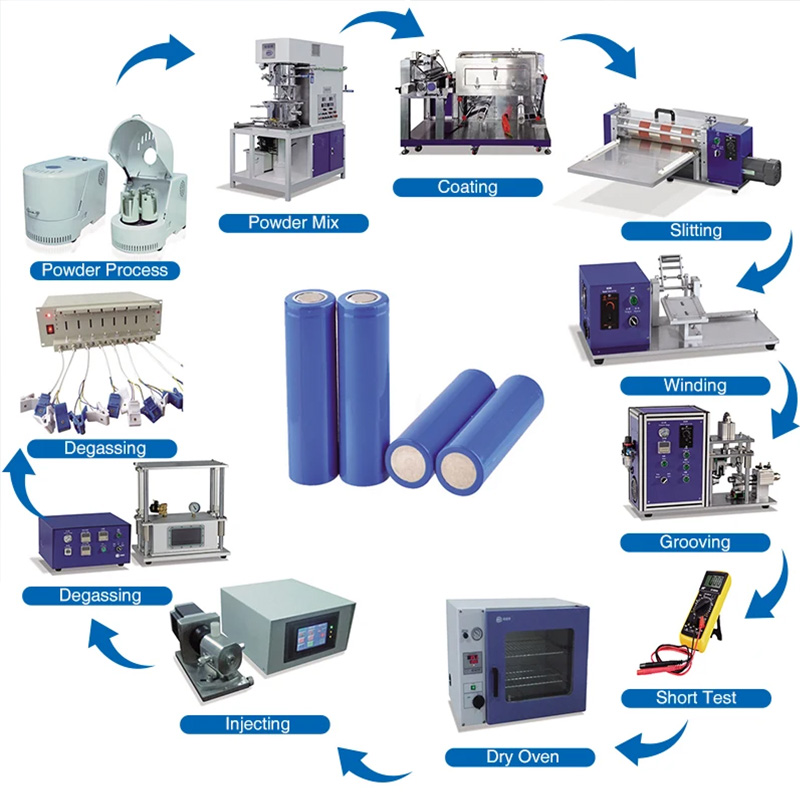
Batteries Step by Step: The Li-Ion Cell Production Process
Introduktion
The production of lithium-ion (Li-ion) batteries is a complex process that involves several key steps, each crucial for ensuring the final battery’s quality and performance. In this article, we will walk you through the Li-ion cell production process, providing insights into the cell assembly and finishing steps and their purpose. Additionally, we will highlight that you can find more information about equipment for Li-ion battery manufacturing on Sovema Group’s website.
18650 21700 26650 32650 Cylindrical Cell produktionslinje
Step 1: Cell Assembly – Electrode Shaping
What is Electrode Shaping?
The cell assembly process begins with finished electrode reels. In pouch and prismatic cells with stacked electrodes, anodes and cathodes are separated from the electrode daughter rolls and cut to size, leaving the current collector as a tab.
Details:
- The electrode cutting can be done through punching (mechanical separation) or laser (thermal separation).
Why Punching?
- Precision
- Affordable initial investment
- Advised for all scales, from labs to mass production
Why Laser?
- Easy format changeover
- Flexibility
- Advised for mass production and well-supported labs
Manufacturing Key Focus Points:
- LASER: The electrode shaping area is subject to heat and requires fume aspiration.
- PUNCHING: Quality issues can arise from burrs on the cutting edge due to tool wear.
Step 2: Cell Assembly – Electrode Stacking
What is Electrode Stacking?
In pouch cells and some prismatic cells, anodes, separator sheets, and cathodes are stacked together in a repeated cycle until the required number of layers is reached.
Details:
- Electrode and separator stacking can use a Z-folding process or a single sheet stacking process.
Manufacturing Key Focus Points:
- Perfect alignment of electrodes and the separator
- Delicate handling of the electrodes to avoid damage to the surface or edges
Step 3: Cell Assembly – Tab Welding
What is Tab Welding?
Between the stacking/winding and packaging stages, the electrical contacting tabs are welded to the electrode current collectors.
Details:
- Different welding methods are used based on cell types (pouch, prismatic, or cylindrical).
Manufacturing Key Focus Points:
- Welding tightness
- Avoid excessive thermal stress during welding
Step 4: Cell Assembly – Packaging (Pouch Cells)
What is Packaging for Pouch Cells?
Once tabs are welded, the cell stack is inserted into the pouch foil. It involves forming a cavity, inserting the stack, sealing, and trimming the excess material.
Manufacturing Key Focus Points:
- Precision of the pouch cavity
- Uniformity of sealing temperature and pressure
- Avoid excessive thermal stress during sealing
Step 5: Cell Assembly – Packaging (Prismatic and Cylindrical Cells)
What is Packaging for Prismatic and Cylindrical Cells?
For these cells, the jelly roll is inserted into metal cans after welding tabs. It involves carving a groove, inserting insulators, and welding.
Manufacturing Key Focus Points:
- Avoid excessive thermal stress during welding
- Delicate handling of the jelly roll
Step 6: Cell Assembly – Electrolyte Filling
What is Electrolyte Filling?
Electrolyte is dispensed into cells, ensuring proper wetting under vacuum conditions. It’s a critical step due to safety and quality considerations.
Manufacturing Key Focus Points:
- Dry room required
- Filling parameters for homogeneous electrolyte distribution
- High hazard level control
- Precise control of electrolyte quantity
Step 7: Cell Finishing – Formation
What is Formation?
Formation is the first charge of the cell, crucial for Solid Electrolyte Interface (SEI) layer formation and battery performance.
Manufacturing Key Focus Points:
- Environmental temperature control
- Efficiency and regenerative technology for cost-effectiveness
Step 8: Cell Finishing – Degassing
What is Degassing?
Gas formed during charging, especially in pouch cells, is removed through degassing and sealing.
Manufacturing Key Focus Points:
- Gas disposal
- Full gas removal from the cell
- Vacuum conditions and dry room requirements
Step 9: Cell Finishing – Aging
What is Aging?
Aging is the final quality control step. Cells are stored and monitored under controlled temperatures.
Manufacturing Key Focus Points:
- Environmental temperature control
- Aging time can be a bottleneck
In conclusion, the production of Li-ion batteries involves a series of meticulously controlled steps, each vital to ensuring the battery’s performance, safety, and reliability.
For more information about equipment for Li-ion battery manufacturing, visit Sovema Group’s website.
Dela med sig
-
Lithium Battery Welding Machine | High-Precision, Fast, SafeNyheterNov.17,2025
-
Aluminium Guide Roller | Anodized, Lightweight, Low-NoiseNyheterNov.17,2025
-
Tofu Cat Litter Bulk – Eco, Low-Dust, Fast Clumping SupplyNyheterNov.17,2025
-
Equipment for Lithium Cell Assembly | Automated & PreciseNyheterNov.10,2025
-
Square File Tool – Precision Cut, Hardened Steel, VersatileNyheterNov.10,2025
-
Lithium Ion Battery Assembly Machine | Automated, High-SpeedNyheterNov.10,2025